The first step in designing a chart is to retrieve the data that you would like to use. Within Chart Designer you can draw data from JDBC/ODBC compliant databases, text files, XML files, EJBs, and even bring in object/array data through class files. All of the data source information is stored within the Data Source Manager.
The Data Source Manager is an integrated utility that stores location and connection information for the data sources employed by a particular user. The information is stored in an XML registry file. You can set up as many different data registry files as you like, and there is no limit to the number of data sources that can be stored within a single registry. The registry is used as an aid at design time, and is not required to deploy charts, since the data or the data source information is stored with the chart file.
![[Caution]](../../../images/caution.png) | Caution |
|---|---|
The XML data source repository only stores location and connection information, and not the actual data. It is not an XML file that contains data to be used in a chart. |
When you start a new chart (by selecting → , or by clicking the button on the toolbar), the chart wizard will launch. The Wizard is a step-by-step process that will guide you through the basic construction of your chart. The first dialog in the chart wizard will prompt you to specify the data registry file that you would like to use, or to create a new registry. By default, data source registry files are saved in the DataRegistry directory. Once you have either opened an existing registry or started a new one, the Data Source Manager window will open.
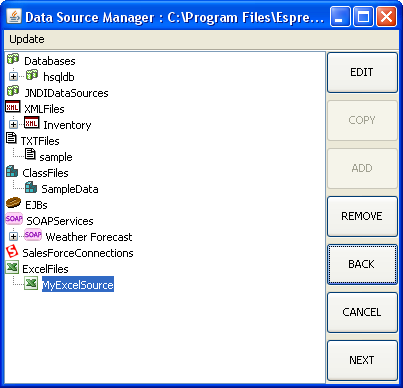
Data Source Manager Window
The left-hand side of the window contains a tree listing all of the data sources in the registry file. Grouped under Databases are the individual databases and their associated queries and data views. Grouped under JNDIDataSources are database sources that use JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface) name to connect instead of JDBC. Grouped under XMLFiles are all the XML files and their associated queries, grouped under TXTFiles are all of the specified Text files, grouped under ClassFiles are all of the specified class files, grouped under EJBs are all the specified EJB connections, and grouped under SOAP are all the specified SOAP data sources.
The right-hand side of the window contains a series of buttons controlling all of the functions of the Data Source manager. Each button performs the following functions.
- Edit:
This allows you to modify attributes of a data source. For a database it allows you to change the connection information, and modify queries/data views. For XML files it allows you to change the file and dtd location, and modify XML queries. For text files it allows you to change the display name, and file location. For class files, it allows you to change the display name and modify the location. And for EJBs it allows you to change the display name, as well as the parameter values.
- Copy:
This option is only available for queries, and data views. It allows you to make a copy of the specified query or data view.
- Add:
This option allows you to add a data source. It will create a new source depending on which node is selected in the left-hand side. Hence, if you select the TXTFiles , and click , you will be prompted to add a new text file data source.
- Remove:
This option will remove the selected data source.
- Back:
This option allows you to go back a step in the wizard, and change the registry file that you are using.
- Cancel:
This will cancel the wizard process.
- Next:
This will use the currently selected data source for the chart, and proceed to the next step in the wizard.